Dysfunction is a broad term used in medical contexts to describe the impaired or abnormal functioning of an organ, system, or part of the body. It can manifest in a variety of ways, depending on the organ or system involved. While the word “dysfunction” is used commonly in medical practice, it is important to understand its specific implications in relation to different conditions, how it affects quality of life, and the treatments available for managing these dysfunctions.
What is Dysfunction?
In medical terms, dysfunction refers to a failure of an organ or system to perform its normal or expected function. This malfunction can occur in any part of the body, from the heart and lungs to the nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and sexual organs. Dysfunction is a broad category that includes a variety of conditions that impair the body's ability to function as intended. It is often used to describe issues that hinder the efficiency of specific organs or physiological processes.
Types of Dysfunction
Dysfunction can affect multiple bodily systems and can be classified into various types. Some of the most common types include:
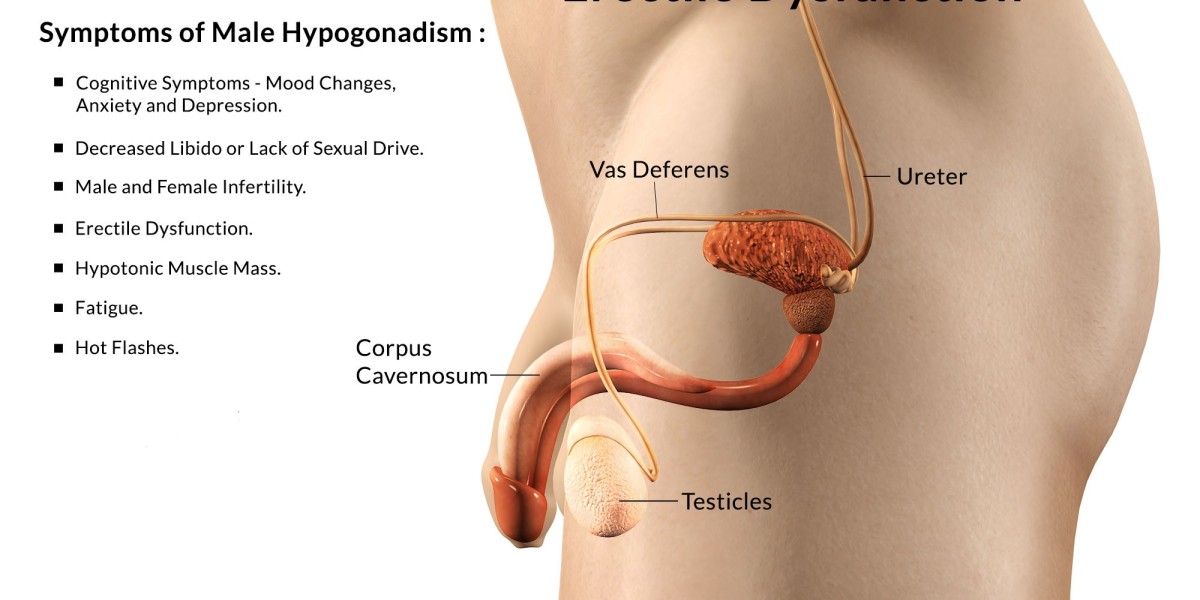
1. Sexual Dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction is a condition in which an individual experiences difficulty with sexual performance or satisfaction. This dysfunction can affect either men or women and can be classified into several subtypes, including erectile dysfunction (ED), premature ejaculation, low libido, and sexual arousal disorders in women.
Erectile Dysfunction (ED): One of the most common forms of sexual dysfunction in men, erectile dysfunction occurs when a man is unable to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. ED can be caused by physical factors such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity, as well as psychological factors like stress and anxiety.
Premature Ejaculation (PE): Premature ejaculation is a condition in which a man ejaculates too quickly during sexual activity, leading to dissatisfaction for both partners.
Low Libido: Low libido refers to a reduced interest or desire in sexual activity. This can be due to hormonal imbalances, psychological factors, medications, or medical conditions.
Female Sexual Dysfunction: Women may experience dysfunction in sexual desire or arousal, which can result from hormonal changes, stress, relationship issues, or underlying health conditions.
Medications such as Lovento 100 mg for women and Kamagra Jelly Online for men are commonly used to address these types of sexual dysfunction. Lovento 100 mg is particularly effective in treating sexual dysfunction in women by enhancing arousal, while Kamagra Jelly Online is a widely used medication for men with erectile dysfunction.
2. Neurological Dysfunction
Neurological dysfunction refers to disorders that affect the nervous system, leading to problems with motor control, sensory perception, cognition, or behavior. Conditions such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy are common examples of neurological dysfunctions.
Stroke: A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted, leading to brain cell damage. This can result in motor deficits, difficulty with speech, vision loss, and cognitive impairment.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS): MS is a chronic disease where the immune system attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, causing nerve damage. This leads to symptoms such as muscle weakness, vision problems, numbness, and coordination difficulties.
Parkinson's Disease: Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement control. Symptoms include tremors, stiffness, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement).
3. Cardiovascular Dysfunction
Cardiovascular dysfunction refers to problems with the heart and blood vessels that impair their ability to circulate blood effectively throughout the body. This category includes conditions such as hypertension (high blood pressure), heart disease, arrhythmia (irregular heartbeats), and heart failure.
Hypertension: High blood pressure is a condition where the force of the blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high. Over time, this can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
Heart Disease: This includes conditions such as coronary artery disease, which is caused by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle.
Arrhythmia: Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats that can lead to problems such as dizziness, fatigue, or even stroke. Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common types of arrhythmia.
Heart Failure: Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump blood effectively to meet the body's needs. It can lead to symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid retention.
4. Gastrointestinal Dysfunction
The gastrointestinal (GI) system is responsible for digestion and the absorption of nutrients. Dysfunction in this system can lead to various symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Common GI dysfunctions include irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, and celiac disease.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is a functional disorder of the digestive system that leads to symptoms such as bloating, cramps, diarrhea, and constipation. It is often triggered by stress, diet, or other lifestyle factors.
Crohn’s Disease: This is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that causes inflammation of the digestive tract. It can lead to symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue.
Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the ingestion of gluten triggers an immune response that damages the lining of the small intestine, leading to malabsorption of nutrients.
5. Endocrine Dysfunction
The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce hormones that regulate various bodily functions. Dysfunction in this system can lead to imbalances in hormone levels, affecting metabolism, growth, mood, and reproductive health. Examples include thyroid disorders, diabetes, and adrenal insufficiency.
Hypothyroidism: This condition occurs when the thyroid gland produces insufficient amounts of thyroid hormones, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
Diabetes: Diabetes is a condition in which the body is unable to regulate blood sugar levels properly. It can lead to complications such as kidney disease, nerve damage, and cardiovascular problems.
Adrenal Insufficiency: This condition occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough of the hormones cortisol and aldosterone, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, and low blood pressure.
Causes of Dysfunction
Dysfunction can arise from a variety of causes, depending on the type of dysfunction being discussed. Some of the most common causes include:
Genetic Factors: Many dysfunctions have a genetic component. Conditions like hereditary heart disease, certain cancers, and neurological disorders can be passed down through generations.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and chronic stress can contribute to dysfunctions in various systems of the body.
Infections and Inflammation: Infections and inflammatory conditions can disrupt the normal functioning of organs and systems. For example, chronic infections in the gastrointestinal tract can lead to dysfunction in digestion.
Hormonal Imbalances: Changes in hormone levels, such as those that occur during menopause, pregnancy, or aging, can cause dysfunction in systems such as the reproductive system and metabolism.
Medication Side Effects: Certain medications can cause dysfunction as a side effect. For example, medications used to treat high blood pressure may cause sexual dysfunction in some individuals.
Treatments for Dysfunction
Treatment for dysfunction depends on the type and underlying cause of the condition. Some of the most common approaches to treatment include:
Medications: Many dysfunctions are treated with medication. For example, Kamagra Jelly Online, a treatment for erectile dysfunction, contains Sildenafil Citrate, which helps men with ED achieve and maintain an erection. Other medications like Lovento 100 mg are used to treat sexual dysfunction in women by increasing sexual arousal.
Lifestyle Changes: Diet, exercise, and stress management can play a significant role in managing and preventing dysfunction. For instance, improving cardiovascular health through exercise and a balanced diet can help reduce the risk of heart disease and hypertension.
Therapy and Counseling: Psychological counseling, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), is often used to treat dysfunctions with a psychological or emotional component, such as depression, anxiety, or sexual dysfunction.
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be required to treat dysfunction. For example, surgery may be needed to correct structural problems in the cardiovascular or gastrointestinal systems.
Hormone Therapy: Hormonal imbalances can often be treated with hormone replacement therapy (HRT), such as thyroid hormone replacement for hypothyroidism or testosterone replacement for men with low testosterone levels.